To prevent this, projects can be developed in concurrent paths, with one path being devoted to the main line of development and others set aside for testing new features or bugfixes. One line can be kept stable or close to stable, with others not yet even in testing. Several common configuration strategies are used for team collaboration on software development.
Ads by Google
Posted by ellen at September 26, 2009 06:11 PM
The field of Software Configuration Management is the discipline of designing methods for effective development team collaboration and version tracking that promote productivity and reduce risk. Branching and merging strategies are software configuration management practices that allow pieces of code to be worked on in isolation from the rest, then later, merged back into the whole. The process of merging involves some extra work and added risk because it can introduce new bugs, but the added productivity of working in the branch often outweighs the extra costs.
There are several commonly used branching strategies. The choice can be determined by the requirements of the project or the workflow preferences of the team. Branches can correspond to phases of development, specific tasks, or particular releases.
Chris Birmele of Microsoft Australia recommends validating your chosen strategy by considering what would happen in a change scenario - would you have to completely restructure your branches to compensate? Try to predict the worst case and plan for it.
A commonly used branching strategy is one that corresponds to the three phases of development activity: Development, Test and Production. For in-depth discussions of branching strategies, see Microsoft Team Foundation Server Branching Guidance: [LINK] or PDF ( license)
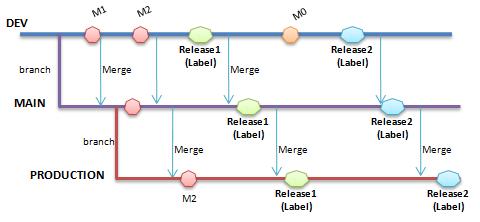
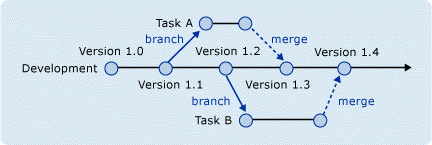
Whichever configuration you choose it's imperative that all team members are on board and fully understand the workflow and best practices associated with tagging, merging, etc. Symptoms of problems with team member's comprehension of the strategy, or of having chosen the wrong structure include avoidance of merging, deferring merges until the very end of the project and general confusion about versions. A longer list of "symptoms" can be seen here [LINK]
The branching structure used in the following tutorial is a task-based branch, where the branch is used for work on a specific tasks. These are short-term branches which are merged back into the main line of development - the Trunk - as soon as the task is completed.

Ads by Google
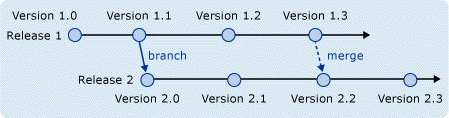
Awsome .... the visual you have provided have added so much of meaning to the words
great work